What is HVLP spray gun?
 HVLP stands for High Volume Low Pressure. An HVLP spray gun is a type of paint sprayer that uses a high volume of air to atomize and spray paint at low pressure, resulting in a smoother and more controlled application of paint with less overspray compared to traditional spray guns.
HVLP stands for High Volume Low Pressure. An HVLP spray gun is a type of paint sprayer that uses a high volume of air to atomize and spray paint at low pressure, resulting in a smoother and more controlled application of paint with less overspray compared to traditional spray guns.
They are commonly used in the automotive and woodworking industries for fine finishing work.
Table of Contents
How does HVLP spray gun work?
An HVLP spray gun uses a high volume of air from an air compressor or turbine to atomize and spray paint at low pressure.
HVLP with Air Compressor – The gun’s air compressor pumps a high volume of air through a hose and into the gun’s air cap. As the air exits the air cap, it creates a low-pressure area that draws paint from the gun’s cup and into the air stream. The paint mixes with the air and is atomized into a fine mist that is then sprayed onto the surface being painted. This process produces less overspray and a smoother, more controlled application of paint compared to traditional spray guns.
Types of HVLP Guns with an air compressor.
- Conventional HVLP: This system uses a separate air compressor to supply air to the spray gun, and the paint is held in a separate cup attached to the gun. The air pressure is regulated at the compressor, and the paint flow is regulated at the spray gun.
- Conversion HVLP: This system converts a standard air compressor into an HVLP spray system by using a conversion gun that replaces the standard air cap with an HVLP air cap. The paint is held in a separate cup attached to the gun, and the air pressure is regulated at the compressor while the paint flow is regulated at the spray gun.
HVLP Gun systems with turbine
Turbine HVLP systems use a turbine motor to generate a high volume of low-pressure air delivered directly to the spray gun, eliminating the need for a separate air compressor. The paint is held in a cup attached to the gun, and the air pressure and paint flow are regulated at the gun. Turbine HVLP systems are generally more portable and easier to set up than conventional HVLP systems. They are commonly used in the automotive and woodworking industries for fine finishing work.
Two types of HVLP Guns – bottom-fed and gravity-fed guns.
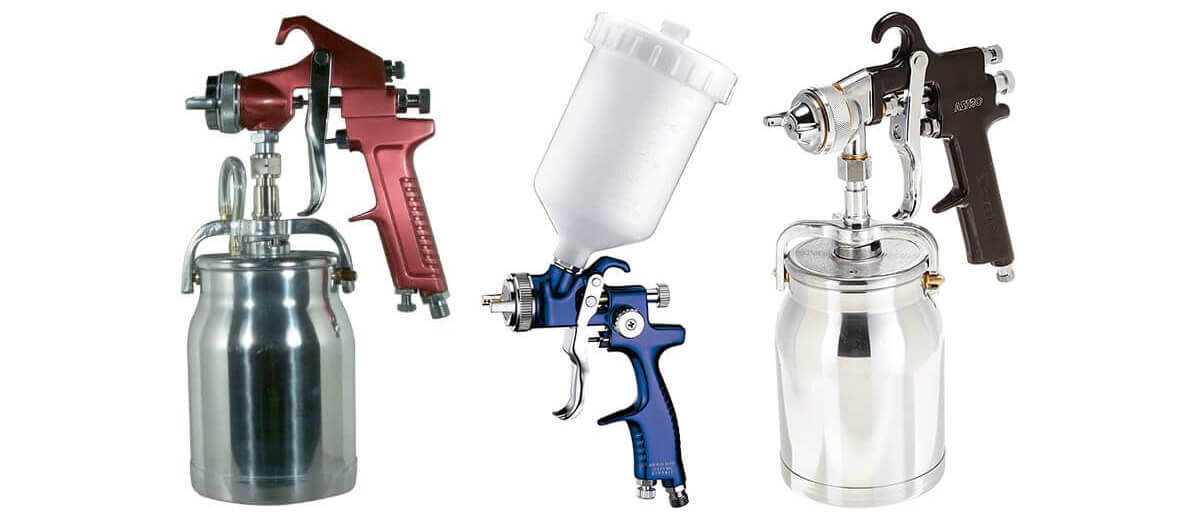 Bottom-fed and gravity-fed guns are two paint spray guns with different paint cup configurations.
Bottom-fed and gravity-fed guns are two paint spray guns with different paint cup configurations.
Bottom-fed – A bottom-fed spray gun has a paint cup attached to the bottom of the gun and is designed to spray heavier materials that require a larger volume of paint. The paint is drawn up from the cup by the force of gravity and fed into the spray gun’s mixing chamber, where it is atomized and sprayed onto the surface.
Gravity-fed – A gravity-fed spray gun has a paint cup on top of the gun and is designed to spray lighter materials requiring a smaller volume of paint. The paint is fed into the gun’s mixing chamber by gravity, which allows for better control of the paint flow and reduces the risk of spills or leaks.
Gravity-fed spray guns are generally preferred for fine finishing work and intricate projects because they provide better control and produce less overspray.
Advantages and disadvantages of HVLP Guns
HVLP guns have several advantages and disadvantages, including:
Advantages:
- Overspray – HVLP guns produce less overspray than traditional spray guns, which means less wasted paint and a cleaner work environment.
- Spray pattern – The controlled spray pattern and reduced overspray of HVLP guns make them ideal for fine finishing work and intricate projects.
- Transfer efficiency – The transfer efficiency of HVLP guns is generally higher than that of traditional spray guns, meaning more of the paint is applied to the surface being painted.
- Cost savings – HVLP guns are generally more efficient and use less paint than traditional spray guns, which can result in cost savings over time.
Disadvantages:
- Larger compressor or turbine – HVLP guns require a larger volume of air than traditional spray guns, so they typically require a larger compressor or turbine system to operate.
- Time spent on setup – HVLP guns may require more time and effort to properly set up and adjust for different types of paint and surfaces.
- Specific application – The slower application rate of HVLP guns may be a disadvantage in certain applications, such as painting large surfaces.
- Equipment cost – The cost of HVLP guns and equipment may be higher than that of traditional spray guns.
HVLP for Precise Control
HVLP guns are often used for precise control in applications that require a fine finish.
Because HVLP guns produce a high volume of air at low pressure, they can be used to deliver a controlled, even spray of paint or other coatings onto a surface. This can be especially useful for tasks such as painting intricate details or applying a clear coat to a surface, where overspray or an uneven application could be more noticeable.
With the right nozzle and pressure settings, HVLP guns can provide precise control over the application of paint, resulting in a professional-looking finish.
HVLP for Cost Effectiveness
HVLP guns can be a cost-effective option for several reasons.
- HVLP guns use less paint than conventional spray guns because they produce a high volume of air at a low pressure that atomizes the paint more effectively. This means less paint is needed to achieve the same coverage, which can result in cost savings over time.
- HVLP guns typically produce less overspray than conventional spray guns, which means less wasted paint and a cleaner work environment. This can also result in cost savings over time by reducing the need for additional paint and cleanup supplies.
- HVLP guns are generally more efficient than conventional spray guns, which means they can complete a job faster and with less effort. This can translate into labor cost savings for businesses or individuals who use them regularly.
But the equipment cost can be higher in most cases.
HVLP system is environment friendly
Less overspray
HVLP guns are generally considered more environmentally friendly than conventional spray guns. This is because they produce less overspray and waste less paint, which means less paint is released into the environment.
Less energy
HVLP guns produce a high volume of air at low pressure; they use less energy than conventional spray guns, which can help to reduce carbon emissions and other environmental impacts.
Low-VOC (volatile organic compounds) paints
Another factor contributing to the environmental friendliness of HVLP guns is that they are often used with water-based or low-VOC (volatile organic compounds) paints, which are less harmful to the environment and human health than traditional solvent-based paints.
Many regulations and guidelines now require the use of low-VOC paints in certain industries. HVLP guns are well-suited to this application because they can atomize the paint effectively, even at lower pressures.
Overall, while no paint application method is completely without environmental impact, HVLP guns are generally considered a more environmentally friendly option than conventional spray guns due to their reduced overspray and paint usage, lower energy consumption, and compatibility with low-VOC paints.
Difference between HVLP and LVLP
HVLP and LVLP are two types of spray guns that are commonly used in painting and finishing applications. The main difference between these two types of guns is the amount of air pressure they use to atomize the paint or coating being sprayed.
HVLP stands for “high volume, low pressure”. HVLP guns use a large volume of air at low pressure to atomize the paint or coating, resulting in a fine mist that can be applied to the surface being painted. This process reduces overspray and paint waste, and also reduces the amount of harmful emissions that are released into the environment. HVLP spray guns are commonly used for automotive painting, furniture finishing, and other applications that require a high-quality finish with minimal waste.
LVLP stands for “low volume, low pressure”. LVLP guns use a lower volume of air at a lower pressure to atomize the paint or coating, resulting in a slower, more controlled spray pattern. This type of gun is often used for touch-up work or other applications that require more precise control over the spray pattern.
Typical paint types for HVLP are Clearcoats, Thin Stains, Lacquers, Varnish, Thinned Latex, etc. LVLP can spray all types of paints that an HVLP can, except latex.
The main advantages of HVLP spray guns over LVLP guns are that they are more efficient and produce less overspray, resulting in less waste and a more environmentally-friendly process. However, LVLP spray guns may be preferred for certain applications where more precise control is required.
Overall, the choice between an HVLP and LVLP spray gun will depend on the specific application and the user’s preferences and experience with each type of equipment.
To summarizes the main differences between HVLP and LVLP spray guns:
| HVLP Spray Guns | LVLP Spray Guns | |
|---|---|---|
| Air Pressure | High volume, low pressure 7-14 psi | Low volume, low pressure 4-10 psi |
| Atomization | Fine atomize paint | Fine atomize paint |
| Spray Pattern | Fine mist | Slower, more controlled spray pattern |
| Efficiency | More efficient, less overspray | Less efficient, more overspray |
| Waste Reduction | Reduces paint waste | Increases paint waste |
| Environmental Impact | Produces fewer emissions | Produces more emissions |
| Applications | Automotive painting, furniture finishing, and other applications requiring high-quality finish | Touch-up work, applications requiring more precise control |
Note: This table is intended to provide a general comparison between HVLP and LVLP spray guns, and individual models and manufacturers may have different specifications and features.
To sum up, HVLP spray guns offer precise control for applications that require a fine finish and are cost-effective and environmentally friendly due to their reduced overspray and paint usage.
There are different types of HVLP systems – air compressors and turbine systems. Choosing the right gun depends on factors such as cup configuration, nozzle size, and air pressure for a specific application.